The most common way of objective cough assessment is the evaluation of cough sensitivity, the responsiveness of cough reflex to external stimuli. A higher cough sensitivity indicates that the cough receptors are sensitized, which results in responses to even weak stimuli that would not induce cough otherwise.
Evaluation methods of cough sensitivity
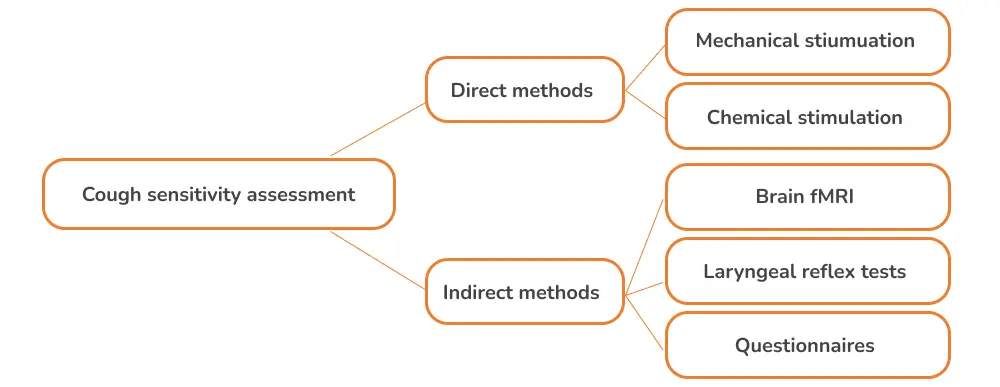
Mechanical stimulation
- Mechanical vibration is used to stimulate the cough receptors.
- The method is simple non-invasive, and safe.
- Some studies indicate that this method can distinguish healthy individuals from patients with cough hypersensitivity, to an extent. Further research is necessary to assess its investigative value.
Chemical stimulation
- Widely used and proven.
- The subject inhales aerosol stimulant particles that further stimulates cough receptors and induces cough.
- Capsaicin is the most preferred chemical stimulant; it can be administrated via a tidal-breath inhalation or a dosimeter-controlled inhalation.
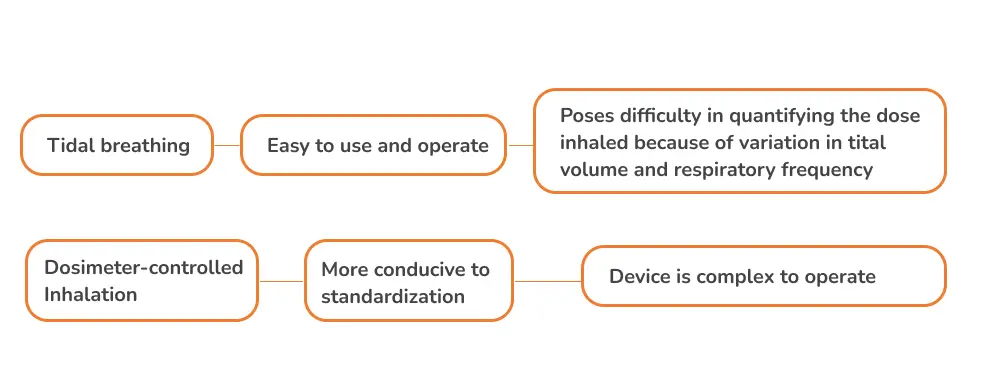
- Factors such as, smoking, obesity, sex, allergic inflammation, TRPV1 polymorphisms, and chemosensory regulation affect cough sensitivity assessment.
Brain fMRI
- A specific sensory organ is stimulated to cause neural activity in the corresponding cerebral cortex, which is detected on fMRI. Thus, fMRI helps in the indirect assessment of cough sensitivity.
- Aids in assessing cough hypersensitivity at the central level and further development of novel antitussives.
Laryngeal reflex tests
- Laryngeal hypersensitivity is an excessive laryngeal response to external stimuli.
- It is an indirect indicator of cough hypersensitivity; this is indicated by resolution of laryngeal irritation after treatment of cough.
- Researchers have developed a novel laryngopharyngeal endoscopic esthesiometer and rangefinder (LPEER); however, the device has been evaluated in patients with swallowing difficulties and not in patients with chronic cough.
Questionnaires
- These reflect cough sensitivity from different perspectives.
- Hull airway reflux questionnaire (HARQ) was developed to evaluate cough sensitivity and diagnose CHS.


